GCN介绍
来自https://www.chainnews.com/articles/216961050590.htm
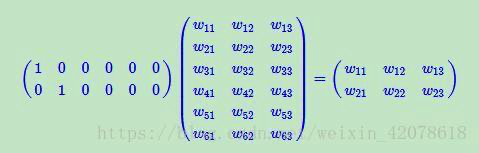
每个节点有自己的特征,假如$N$个节点,每个节点特征维度为$D$,特征矩阵($X$)的形状就是$N\times D$。同时有一个邻接矩阵$A$,形状是$N\times N$。
层之间的传播方式是:$H^{(l+1)}=\sigma\left(\tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} H^{(l)} W^{(l)}\right)$
- $\tilde{A}=A+I$
- $\tilde{D}{i, i}=\sum\limits_j \tilde{A}{i, j}$
- 第一层的话,$H$就是$X$
GCN里面的$\tilde{A}$的处理是为了能够处理节点自己本身的特征,$A$里面本身对角线是0就导致用$A$无法捕获节点本身的特征。
GCN的基本思路
来自 https://www.zhihu.com/question/54504471/answer/332657604
CNN无法处理Non Euclidean Structure的数据,无法在图上用一个相同尺寸的卷积核进行卷积;但是又想要提取空间特征进行机器学习。
提取空间特征可能用:
- Vertex domain(spatial空间的 domain):找neighbors,neighbors的attributes就是channels
- Spectral domain(谱的)借助于图的拉普拉斯矩阵的特征值和特征向量来研究图的性质
- 可能是$L=D-A$,$L^{sys}=D^{-\frac{1}{2}}LD^{-\frac{1}{2}}$,$L^{rw}=D^{-1}L$
- 拉普拉斯矩阵是对称矩阵,可以进行特征分解(谱分解);拉普拉斯矩阵只在中心顶点和一阶相连的顶点上(1-hop neighbor)有非0元素,其余之处均为0;与拉普拉斯算子可以进行类比(https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/85287578 )
- 拉普拉斯算子可以从传播的角度考虑。节点$i$受到的影响其实是 所有邻居与它的差 的综合,所以是$\Delta f_{i}=\sum_{j \in N_{i}} W_{i j}\left(f_{i}-f_{j}\right)$,进而写成$d_if_i-w_i\cdot f$。 拉普拉斯矩阵中的第$i$行实际上反应了第$i$个节点在对其他所有节点产生扰动时所产生的增益累积
理解GCN
如何理解 Graph Convolutional Network(GCN)? - superbrother的回答 - 知乎
https://www.zhihu.com/question/54504471/answer/332657604
离散卷积本质上就是加权求和。
Spectral graph theory:借助于图的拉普拉斯矩阵的特征值和特征向量来研究图的性质
常用的拉普拉斯矩阵实际有三种
(1)拉普拉斯矩阵是对称矩阵,可以进行特征分解(谱分解),这就和GCN的spectral domain对应上了
(2)拉普拉斯矩阵只在中心顶点和一阶相连的顶点上(1-hop neighbor)有非0元素,其余之处均为0
(3)通过拉普拉斯算子与拉普拉斯矩阵进行类比(详见第6节)
系列文章GNN-algorithms
https://github.com/wangyouze/GNN-algorithms
斯坦福Machine Learning with Graphs学习笔记
Pytorch实现
https://github.com/FighterLYL/GraphNeuralNetwork/tree/master/chapter5